Creating a Sustainable City (#SDG 11): A Collaboration Between NM Gifted Elementary Students and PA 10th Graders
During Spring, 2022, a student in my gifted education program suggested that they build a paper city. I loved the idea, suggested that they make a sustainable city, and gave them some additional resources to do so. It ended up being amazing (for more about this see Building a Sustainable City and Class Example of a Sustainable City).
Along with teaching these gifted elementary students (who I teach for multiple years), I teach graduate courses for Walden University. One of the courses is Innovative Curriculum. During the course, these graduate students are asked to develop a global networked curriculum where two groups from very diverse geographical locations, preferably a country different than one’s own, work to solve an authentic problem. Raelee Sweigart a former math teacher and now math coach at Reach Cyper Charter School, developed a curriculum about the two groups of high school students using geometry to create model sustainable housing. Of course, I went a little crazy as my elementary students just finished their sustainable city model. I suggested we use her curriculum to do a collaboration whereby her high school students from throughout Pennsylvania work with my gifted upper elementary students in Santa Fe, New Mexico (two very different geographical and cultural locations). My students wanted to rebuild and refine their city this year, and what a fantastic way for both groups to learn applied geometry. I am so excited. Below is the highlights of our collaboration. Thank you, Raelee!
Overview of the Project (developed by Raelee)
During one of the Innovative Curriculum modules, students are asked to develop a digital handout of the project to share with students. Here is the one created by Raelee and modified for our collaboration: https://www.canva.com/design/DAFX8rX_03g/Vm_nSf6_RkTxgjoV99gWmA/view.
Padlet Introductions
As Raelee suggested in her model project, the students introduced themselves using a Padlet. She included columns for video introductions as wells as ones for students to post images of their geographical locations. I later suggested that she add columns for students to post images of example sustainable building from their geographical locations.
Screencast of Our First Meeting
This is a snippet of our first Google Meet together, when the students from the two schools met each other and Raelee reviewed the project.
Tinkercad Tips
Our second session focused on Tinkercad tips as that is the tool the students are using to create their sustainable city structures. Here is an edited clips of this meeting:
Sustainability Presentation
- Recording: https://screencast-o-matic.com/watch/c0nrrTVyOtf
- Slides: https://www.canva.com/design/DAFapgemzww/JlYdsK-WfLa19s0f5Yr4fQ/view
Support Handouts
The support documents for this project were found at I love Projects. Geometrocity, the City Made of Math http://digitaldivideandconquer.blogspot.com/2014/07/i-love-projects-geometrocity-city-made.html
10th Grade PA Students Teaching NM Elementary Students
The Pennsylvania students spent several of our meetings teaching the New Mexico students some geometry concepts related to 3D rendering and building construction.
Raelee created a Classkick, a formative assessment tool, for students to review geometry concepts – https://app.classkick.com/#/public/assignments/AYb6pKCnTQyMJFEKeSdp3w.
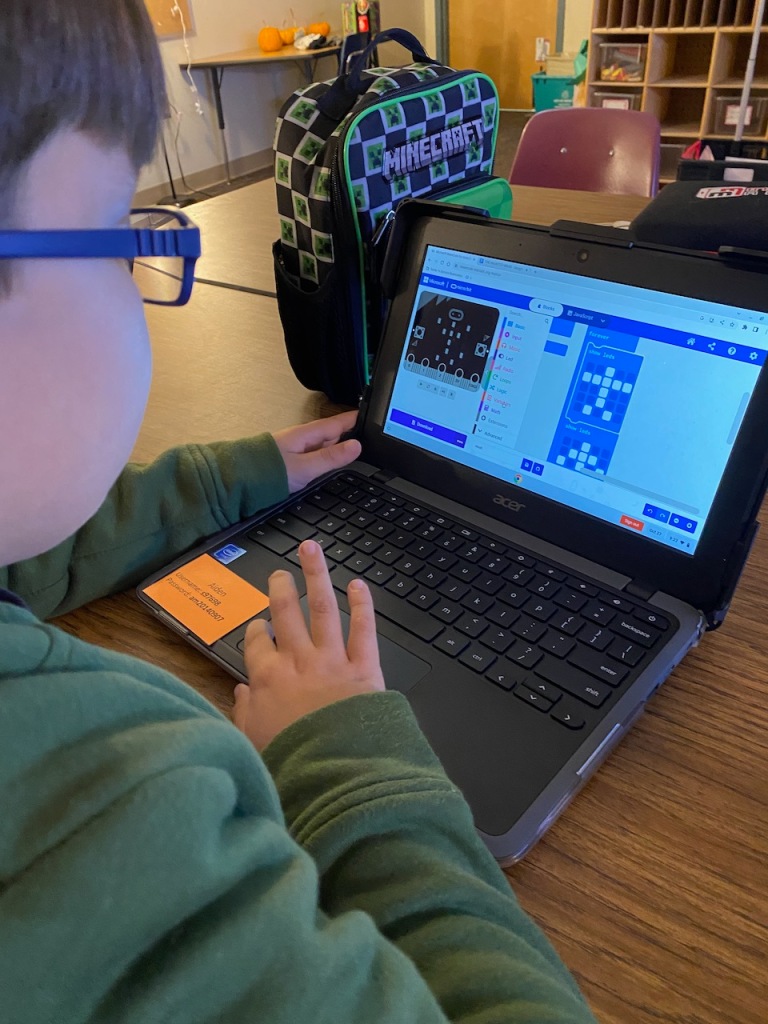
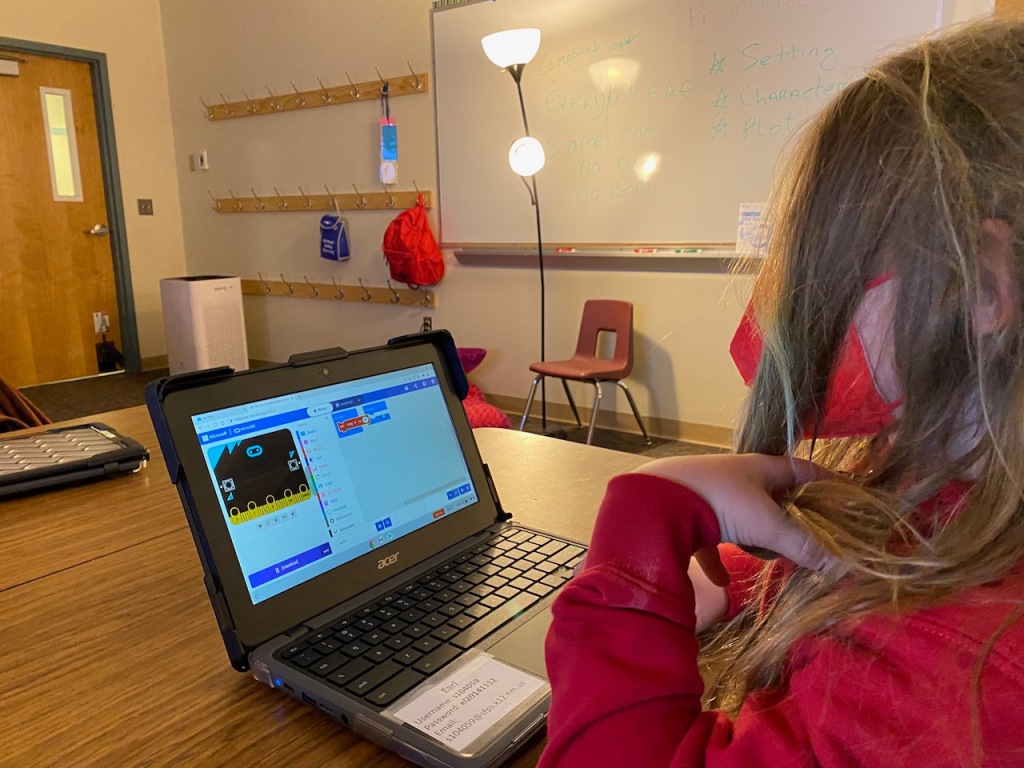
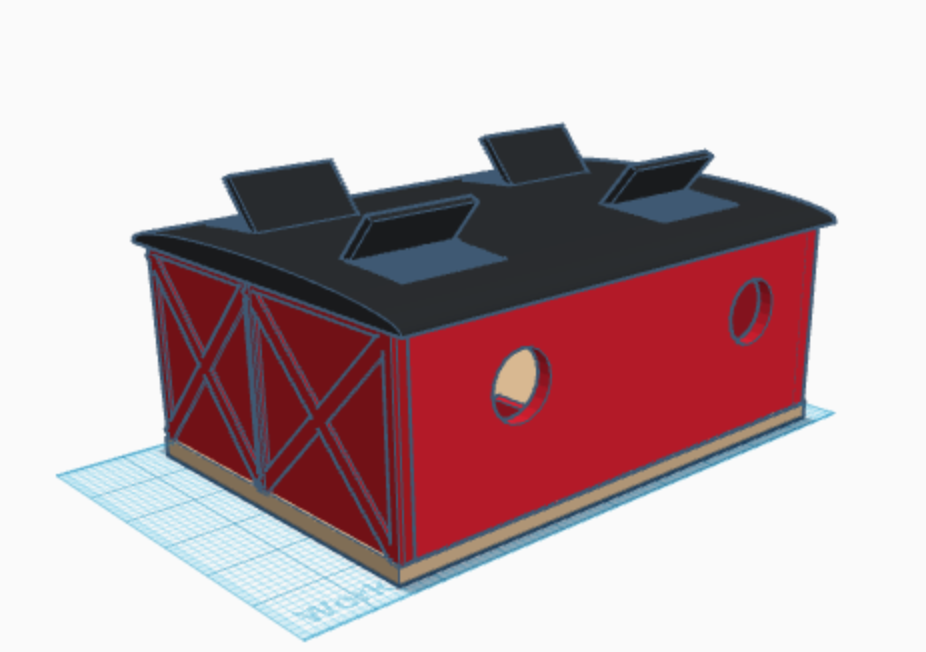
Working Collaboratively in Tinkercad to Design Sustainable Buildings
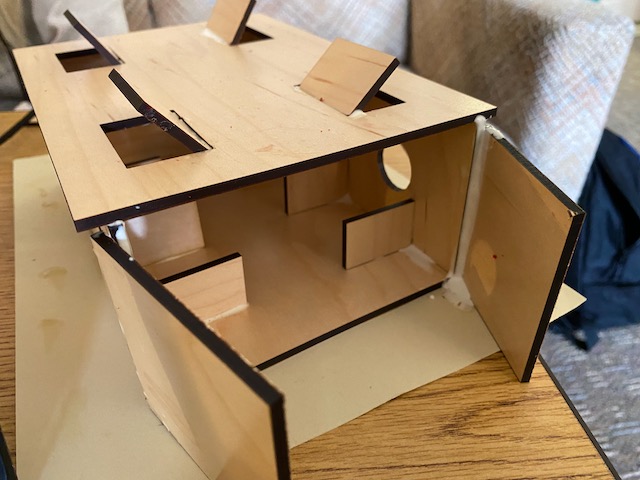
The group worked in Tinkercad, an online 3D modeling program that permits collaboration, to create their buildings. The New Mexican students worked with a scale of .25″/1′ in order for the buildings to work with their sustainable city model.
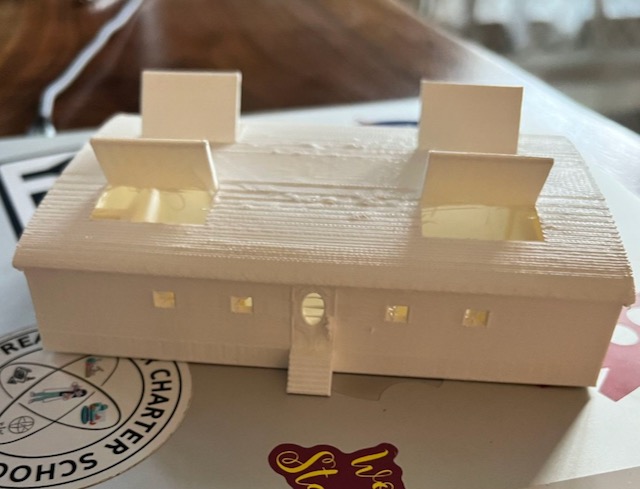
Making the Sustainable Buildings
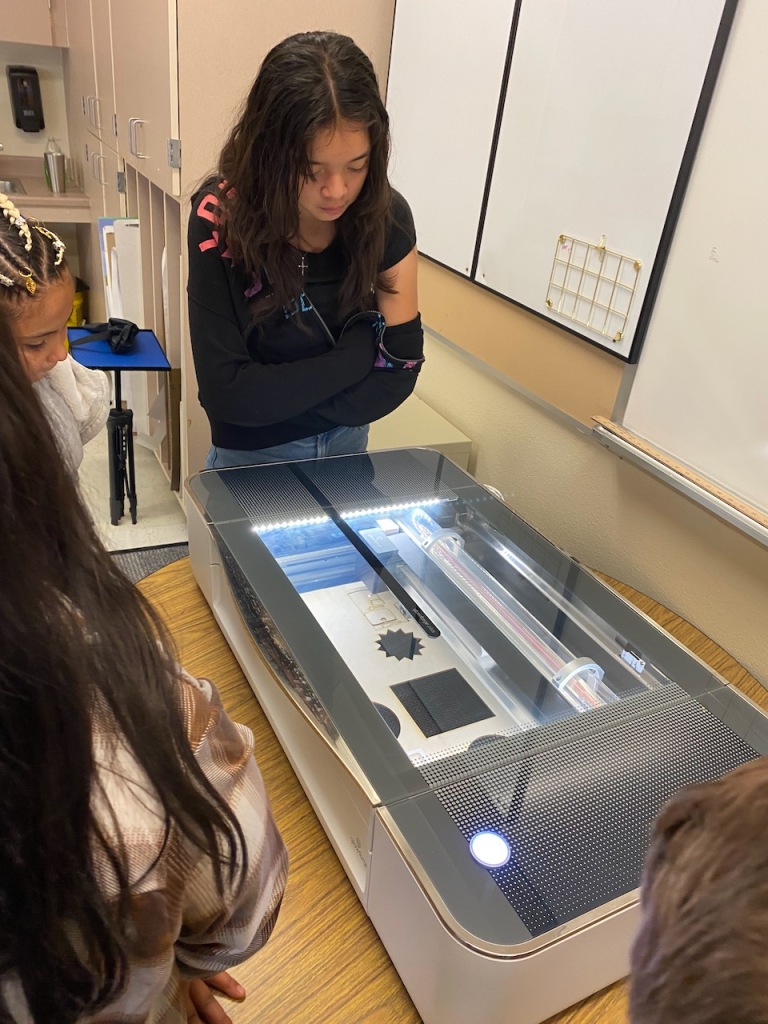
Students in New Mexico will use a laser cutter to create the major parts of their sustainable buildings. In Pennsylvania, the buildings will be 3D printed for the students.
Final Slide Presentations
During our final session, student groups gave slide presentations. Below is their slide decks and oral presentations.
Upper Elementary NM SAGE Students’ Final Sustainable City
The New Mexico students using the buildings created through this project to build a sustainable city. The city was displayed in our school foyer. They explained it to several classes.
They used Canva to make poster to go along with their display:
ChatGPT in the Classroom
I love educational technology. When technologies were first available online, I was an early adopter, and often got brutally criticized by administrators and colleagues in my K-6 settings for having students use the internet for research, use web tools, create webpages in wikis, and work virtually with schools in other states and countries (for example, see their work from 2008 at http://weewebwonders.pbworks.com/). Now, similar work is often seen as innovative by colleagues. Boy, have times thankfully changed, but I have not. I still am an early adopter of technologies in that I believe many can benefit students in their learning.
As many in education know, commentary about ChatGPT is appearing on the news, social media, and the internet. As I always do, I am exploring its use in my classes (elementary-level gifted education). This post describes its use in education from the perspectives of ChatGPT, itself, and from a handful of educators. Later, I describe and show the work of my students. I conclude with tools for detecting machine-generated text, and provide a parting shot.
General Ideas for Using ChatGPT in Education
ChatGPT, according to ChatGPT, is a variant of the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) language model that has been specifically designed for generating human-like text for chatbot applications. GPT models are trained on large amounts of text data and are able to generate natural language text that is coherent and grammatically correct. ChatGPT is trained to generate text that is more conversational and appropriate for use in chatbot applications. It can be used to generate responses to user input, initiate conversations, and provide information and assistance to users in a chatbot setting.
According to ChatGPT, there are several potential ways that ChatGPT or similar language models could be used in education:
- As a tutor or teaching assistant: ChatGPT could be used to provide personalized feedback and guidance to students, answering questions and providing explanations on a variety of educational topics.
- For language learning: ChatGPT or similar models could be used to provide conversation practice and feedback to students learning a new language.
- To generate personalized learning content: ChatGPT or similar models could be used to generate customized learning materials for students, such as practice problems or reading assignments.
- To facilitate collaborative learning: ChatGPT or similar models could be used to facilitate discussions and collaboration among students, providing prompts and guidance for group projects and assignments.
Here are some guides created by educators, Torrey Trust and Andrew Herft, for using ChatGPT in educational settings. They include uses for teachers such as creating lesson plans and assessments as well as how students can use it:
Angela Watson wrote a guide on how ChatGPT can reduce a teacher’s workload:
ChatGPT in the K-12 Setting
When specifically asked how ChatGPT can be used by K-12 students, it reported the following:
K-12 students can use ChatGPT in a variety of ways to enhance their learning experience. Some examples include:
- Asking ChatGPT to explain a difficult concept or topic
- Using ChatGPT to generate practice questions and answers for studying
- Asking ChatGPT to summarize a text or article
- Using ChatGPT to generate creative writing prompts
- Asking ChatGPT to help with homework by answering questions or providing explanations
- Using ChatGPT to improve reading comprehension by asking questions about a text
- Creating interactive quizzes and games to make learning more engaging
It also (thankfully) provided a disclaimer: It’s important to note that while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool for K-12 students, it should not be used as a substitute for a teacher or other educational professional. A teacher can help to provide guidance, feedback, and structure to the learning process.
Matt Miller of Ditch the Textbook also discussed uses of ChatGPT in K-12 education:
More detailed explanations of these can be found in ChatGPT, Chatbots and Artificial Intelligence in Education. Since the time this blog post was first composed, Matt has written a book – AI for Educators: Learning Strategies, Teacher Efficiencies, and a Vision for an Artificial Intelligence Future which can be purchased on Amazon.
ChatGPT Can Support Students’ Social Emotional Learning
Students and teachers may benefit from asking and discovered various ways it could assist someone with social and emotional skills. It gave helpful answers to all the questions below, and when asked to “regenerate the response” was able to provide additional quality responses. It can be very helpful for anyone who has a difficult time in social situations, is nervous about making friends, is conflicted about how to handle a particular situation.
- What are some questions I could ask a new friend?
- What advice do you have for someone starting a new school and wanting to make friends?
- What are some suggestions for how to say no if a friend asks to copy my homework?
- What are suggestions to explain to someone what they said or did hurt my feelings?
- What are small talk suggestions at a party?
- I am nervous about my test tomorrow; can you give me some relaxation strategies?
- I want to motivate my group members to help with our project; what are some suggestions to help motivate them?
- I made the soccer team, but my best friend didn’t make it, I feel bad and don’t know what to do. Do you have any suggestions?
- I want to practice being kind in the new year. What are some specific ways I can show kindness to others? (ChatGPT to Your Classroom-your-classroom/).
Testing ChatGPT with My Students
In his blog post, ChatGPT, Chatbots and Artificial Intelligence in Education, Matt proposed that maybe ChatCPT should be blocked until the end of the school year because, “We need some space. Some time. A little room to ponder, to sit with all of this. To talk to other educators about what they think. To talk to students and to parents.” For me, the best way to find out about the functionality and effectiveness of any potential classroom-based educational technology is to have students test it out for themselves, so that is what I did with my 4th-6th graders.
I think it is important to be intentional when any educator or I use any type of educational technology. I get frustrated when I see conference presentations about 50 educational technologies in 50 minutes. It becomes about the tool rather than about the pedagogy. When using educational technology in the classroom, instructional goals should be established beyond just learning about the tool. As such, when I asked students to explore ChatGPT, I had two purposes in mind, (1) To be critical consumers of online tools, and (2) To increase their joy of the written word.
They were given the following task:
- Test out ChatGPT (using my account under my supervision) with two of the following
- A Piece of Your Own Writing
- Favorite Book
- Favorite Song
- Current News Story
- Historical Event
- (My students ended up using it to create a written piece to go with an image generated by DALL·E 2, a new AI system that can create realistic images and art from a description in natural language.)
- For each, try to
- Create a rap or rock song.
- Write a three act play, TV show, or movie. Specify the characters.
- Create a fairy tale.
- Write a limerick.
- Create a newscast.
- Create a holiday.
- Create a commercial.
- Make a joke.
- Get feedback.
- Rules
- No violence.
- No fighting characters.
- Focus on the positive and kindness.
Students then wrote a blog post that included their results as well as reflections on the following questions:
- Did it produce desirable results? If so, to what degree? If not, why?
- What did you like best?
- Do you think it will lose its novelty? Why or Why not?
- How can it help you learn better?
- Why shouldn’t it ever be used in school?
Here is a slide deck of their work that they posted on their Fan school blogs (note: I instructed them to indicate that the images and text were generated by AI:
A summary of my students comments about using ChatGPT at school:
- ChatGPT should not be used in school because then kids will use it instead of writing themselves, which defeats the purpose of practicing to write, a skill that is vital in later life.
- On the other hand, it could help me learn proper grammar and advanced words.
- It can help you learn by giving you examples and thoughts.
- The results were very desirable because it was very good grammar and a realistic image, I rate it a ten.
- I think this website will help me learn better by including proficient and highly advanced words.
- I think ChatGPT should never be used in school because it takes no work other than typing a few words into a search bar and then you push a button and the website does all the work for you.
- I think a reason why you should not use this for school work is because you will get in trouble.
- I like it because it is so cool the way that it creates a story just by describing something.
- I think you shouldn’t use AI at school because you are basically cheating.
I then asked students to create a pledge for using ChatGPT for work related to school:
Detecting Machine-Generated Text
Teachers, rightfully, are fearful of the potential for students to cheat using ChatGPT to generate essays, homework assignments, etc. To help offset this problem, apps and tools are being develop to help detect
- GPTZero.me rolled out their new model that includes sentence highlighting and much faster processing. GPTZero now highlights sentences for you that are more likely to have been written by AI, a key feature that teachers have been requesting. File uploads have been added You can upload a PDF, docx, or txt file where GPTZero will read the text and detect AI plagiarism!


- The AI Text Classifier, by openai, the developers of Chat GPT, is a fine-tuned GPT model that predicts how likely it is that a piece of text was generated by AI from a variety of sources, such as ChatGPT.
- AI Writing Check is a free service developed by Quill.org and CommonLit.org to enable educators to check if a piece of writing submitted by a student was written by the AI tool ChatGPT. This algorithm is designed to detect AI-generated writing. We estimate, based on testing with 15k essays, that this tool is accurate 80-90% of the time. For this reason, we’d like to encourage teachers to exercise caution when using this tool to detect academic dishonesty. AI Writing Check is a stopgap tool measure for educators to use this school year until more advanced AI detection tools are made widely available.
- Giant Language Model Test Room (or GLTR) is another tool that can be used to predict if casual portions of text have been written with AI. To use GLTR, a piece of text simply copy and pasted into the input box and anaylze is hit to generate a report.
Citing ChatGPT
With my elementary students, I simply ask/require that they cite that they used ChatGPT (and Dall-e) in their blog posts which is their writing platform.
For my graduate students, this isn’t an issue yet, but has the possibility of being so. Scribber has these suggestions for citing ChatGPT:
How to cite ChatGPT in APA Style
APA doesn’t have a specific format for citing ChatGPT content yet, but they recommended in a tweet that it should be cited as a personal communication, since the text is not retrievable (chats are unique to each user, so you can’t provide a URL for others to access your chats).
Universities and citation authorities are still working out if and when it’s appropriate to cite ChatGPT in your work. There isn’t a clear consensus yet. Always check your institution’s guidelines or ask your instructor if you’re not sure.
If you’re using ChatGPT responses as a primary source (e.g., you’re studying the abilities of AI language models), you should definitely cite it for this purpose, just as you would any piece of evidence.
If you use ChatGPT to help you in the research or writing process (e.g., using it to develop research questions or create an outline), you may be required to cite or acknowledge it in some way. Check if your institution has guidelines about this.
Don’t cite ChatGPT as a source of factual information (e.g., asking it to define a term and then quoting its definition in your paper). ChatGPT isn’t always trustworthy and is not considered a credible source for use in academic writing.
How to cite ChatGPT in APA Style. APA personal communication citations don’t require a reference entry. Instead, they’re mentioned in parentheses in the text wherever you quoted or paraphrased the source.Example: APA ChatGPT citation(ChatGPT, personal communication, February 16, 2023)
ChatGPT Citations | Formats & Examples – https://www.scribbr.com/ai-tools/chatgpt-citations/
Better Yet – Design ChatGPT-Proof Learning Activities
For years many educators have talked about having students do Google-proof activities. To do so, Doug Johnson suggested:
- Allow (or require) the student to relate the academic topic to an area of personal interest.
- Allow (or require) the student to do inquiry that has implications for him/herself or his/her family.
- Allow (or require) the student to give local focus to the research.
- Allow (or require) that the student’s final product relate to a current, real-world problem.
These suggestions are applicable to ChatGPT. Similar ideas were suggested by Alyson Klein in Outsmart ChatGPT: 8 Tips for Creating Assignments It Can’t Do:
- Ask students to write about something deeply personal – Consider having students delve into their scariest moment, the biggest challenge they ever overcame, or even answer a quirky personal question: Would you rather be the bucket or the sand? It’s difficult at this point for AI to fake highly personal writing.
- Center a writing assignment around an issue specific to the local community. ChatGPT doesn’t have a strong background in hyperlocal issues, though that is likely to change as the tool becomes more sophisticated, experts say. But for now, educators may be able to minimize how much help ChatGPT can be on a particular assignment by grounding it in the school community—maybe even by asking students to write about a new school rule or the student council election.
- Direct students to write about a very recent news event. At this point, ChatGPT can’t capture much information about things that happened just days earlier. Teachers could ask students to compare a very recent news event to a historical one.
- Have students show or explain their work. In math class, students usually show how they arrived at a particular answer to get credit for solving a problem. That concept could apply to writing. For instance, teachers could prompt students to detail their brainstorming process, explaining why they choose to write about a particular topic. Have students show or explain their work. In math class, students usually show how they arrived at a particular answer to get credit for solving a problem. That concept could apply to writing. For instance, teachers could prompt students to detail their brainstorming process, explaining why they choose to write about a particular topic.
- Ask students to give an oral presentation, along with the written work. Ask students to record themselves on a video platform such as FlipGrid, talking about their essay, story, report, or other assignment,
To these ideas, I add:
- Have students write during class time (which is my preference anyhow).
- Have students create their writing piece as part of a poster or Infographic (with graphics) using an online tool such as Canva, Adobe Express, and/or Book Creator.
- Have students create an art piece (2D or 3dD) to go along with the writing and explain how it does so.
- Ask students to do collaborative writing using Google Docs that is a truly integrated piece (not individual pieces) from several students.
- Allow students to use ChatGPT with students giving it credit, analyzing it, and adding their own ideas.
Parting Shot
Many of the same fear and arguments that are being leveraged against ChatGPT in education settings have been leveraged against other technologies in the past. Wikipedia is one of those examples. I loved it when it first came out, but I knew lots of teachers who banned Wikipedia in their classrooms.
“Big-picture, AI will cause a shift students will deal with for the rest of their lives. They’ll wrestle with questions of humanity, questions of obsolescence, ethical questions. Let’s [teachers] help them with this” (http://ditch.link/ai via @jmattmiller).
The presence of disruptive technologies like ChatGPT should cause us to reflect on our learning goals, outcomes, and assessments, and determine whether we should change them in response, wall off the technology, or change the technology itself to better support our intended outcomes. We should not let our existing approaches remain simply because this is the way we have always done them. We should also not ruin what is great about writing in the name of preventing cheating. We could make students hand-write papers in class and lose the opportunity to think creatively and edit for clarity. Instead, we should double down on our goal of making sure that students become effective written and oral communicators. For better or worse, these technologies are part of the future of our world. We need to teach our students if it is appropriate to use them, and, if so, how and when to work alongside them effectively (Advice and responses from faculty on ChatGPT and A.I.-assisted writing)
These technology-driven disruptions will not be smooth, even if they can make us better off in the long run. Among the worst things we could do would be to let the drawbacks of these technologies deny us their benefits. In addition, the net effect of these changes will not be felt equally, so we all had better improve our capacity for compassion soon. The impact of ChatGPT and similar tools on education and the workforce may not yet feel much different than the trends of recent decades, but the depth and breadth of the changes brought by AI tools is accelerating and may be something new entirely (With ChatGPT, Education May Never Be the Same).
Winter Holiday Display: A Great STREAM Project
I love celebrating the holidays and calendar events with my gifted students from my bilingual, Title 1 school. I ask them to make artifacts and displays that showcase both their talents and the holiday (see my blog posts about Dia de las Muertos and Pi Day for examples.) Not only are the projects fun, engaging, and exciting, they also provide opportunities for students to gain STEM/STEAM/STREAM knowledge and skills that address interdisciplinary standards. For this year, 2022, they created displays that included components for Christmas, Hanukah, and Kwanzaa. To do so, they . . .
- researched different components of the holidays, and created posters to go with the displays
- used art and engineering to make kinaras, gingerbread houses, and dreidels
- wired and used LEDs to light up their kinaras and gingerbread houses
- programmed micro:bits and Circuit Playgrounds to go with their displays
Introduction
I live in New Mexico. Knowledge of Hanukah and Kwanzaa is limited by our state population. so I began this project with holiday themed Kahoot quizzes (the kids love Kahoots). I think Kahoot quizzes are a great way to introduce new information to students. Here is a list of the ones I did with students:
- https://create.kahoot.it/share/winter-holidays/0a011bba-b79e-4044-9374-af7092aacc80
- https://create.kahoot.it/share/winter-holidays/332f63a4-e53d-45a1-8c87-c2328244c78d
- https://create.kahoot.it/share/winter-holidays-around-the-world/939312a6-cbca-4e4e-abdd-777433dc9846
During the quizzes, I visited websites to show students more information about the content being covered.
- Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and domain specific words and phrases, including those that signal precise actions, emotions, or states of being and that are basic to a particular topic.
Researching the Different Winter Holidays
This is is the R in STREAM which translates into reading and writing. “STREAM adds one more layer to STEM and STEAM: reading and wRiting. Advocates of STREAM see literacy as an essential part of a well-rounded curriculum, as it requires critical thinking as well as creativity. STREAM projects are similar to STEM or STEAM, but fold in the components of reading and writing” (STEM vs. STEAM vs. STREAM: What’s the Difference?).
After selecting from a list of holiday-related topics, students researched, selected key points, and found applicable images to create posters for the displays. Here are the posters they created (noting that we are a bilingual Spanish class so some of them are in Spanish):
- Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects based on focused questions, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
- Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
- Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and domain specific words and phrases, including those that signal precise actions, emotions, or states of being and that are basic to a particular topic.
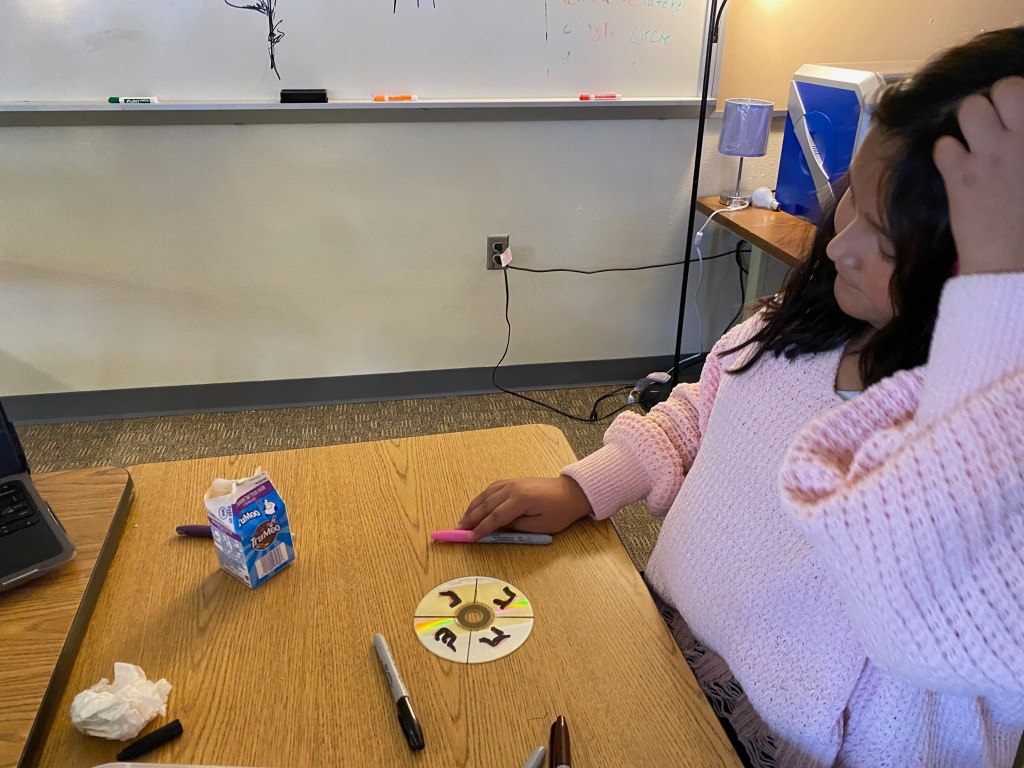
Hanukah Dreidels
Kathy Ceceri developed the Circuit Playground Dreidel – https://learn.adafruit.com/CPX-Mystery-Dreidel/overview. Kathy has them cut out their cardstock dreidels from a PDF. I created a template in Cricut so they could be cut out ahead of time. Here is a link to it https://design.cricut.com/landing/project-detail/6380fecebf31eaf51e587127. Due to the complexity of the code, students were provided with the one developed by Kathy.
Another kind of dreidel was made using CDs – see https://minds-in-bloom.com/make-dreidel-out-of-cd/.
Finally, students get to play the dreidel game (happening this coming week).
Standards Addressed
Next Generation Science Standards – Engineering
- Define a simple design problem reflecting a need or a want that includes specified criteria for success and constraints on materials, time, or cost.
- Social studies programs should include experiences that provide for the study of culture and cultural diversity.
- Anchor Standard #1. Generate and conceptualize artistic ideas and work.
- Anchor Standard #2. Organize and develop artistic ideas and work.
- Anchor Standard #3. Refine and complete artistic work.
Making Kinaras
“The kinara is a seven-branched candleholder used in Kwanzaa celebrations in the United States. During the week-long celebration of Kwanzaa, seven candles are placed in the kinara—three red on the left, three green on the right, and a single black candle in the center. The word kinara is a Swahili word that means candle holder. The seven candles represent the Seven Principles (or Nguzo Saba) of Kwanzaa. Red, green, and black are the symbolic colors of the holiday” (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinara).
Students created the kinara by making tissue paper candle holders to make the kinara candles. See the Lighting section below on how they were lighted.
Standards Addressed
- Social studies programs should include experiences that provide for the study of culture and cultural diversity.
Making Gingerbread Houses
Making gingerbread houses is typically associated with Christmas time and it is a great activity for students. I purchased kits at deeply discounted websites like Five Below prior to the Christmas session. This means that the kits are quite old but they aren’t for eating, they are for display. To add another element of fun, I cut out the doors and filled them with Isomalt. This permitted students to add lights inside to micmic how a house might look like during Christmas (see next section on lighting).
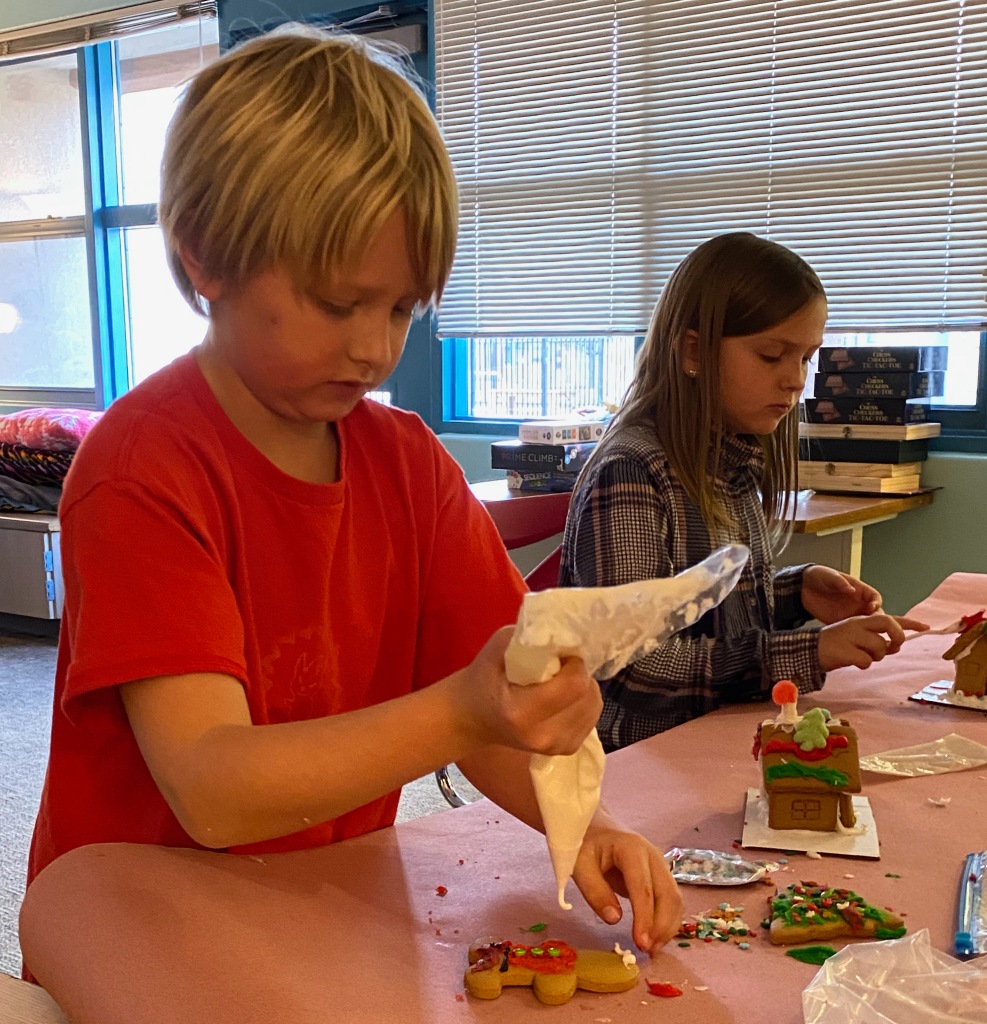
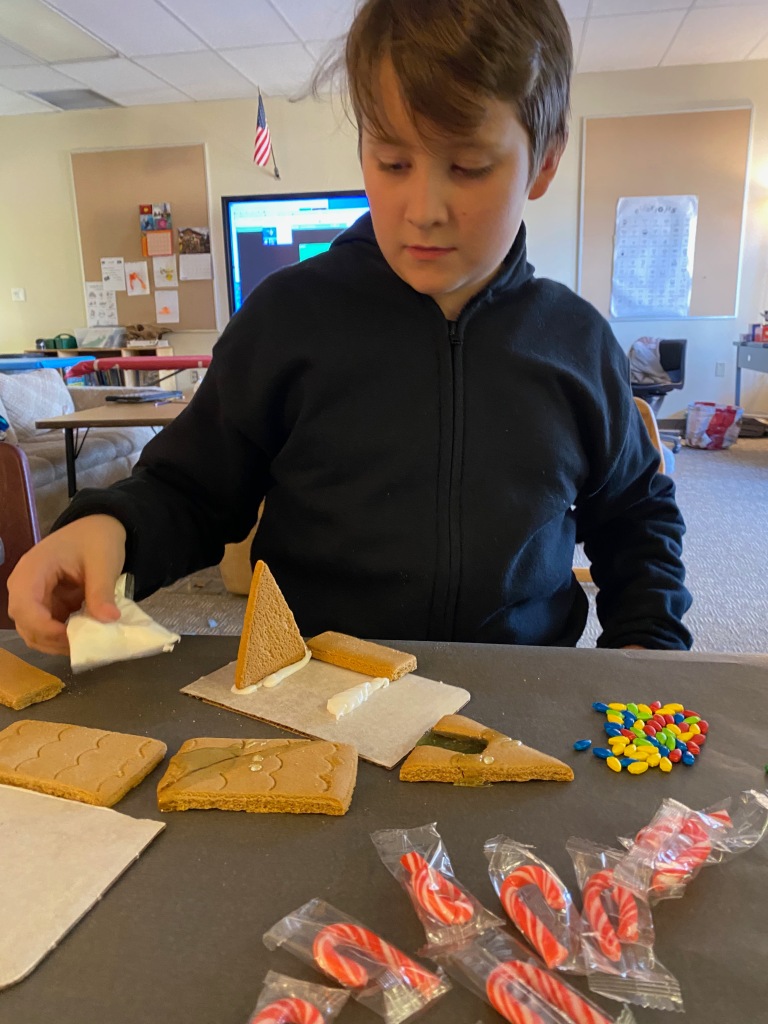
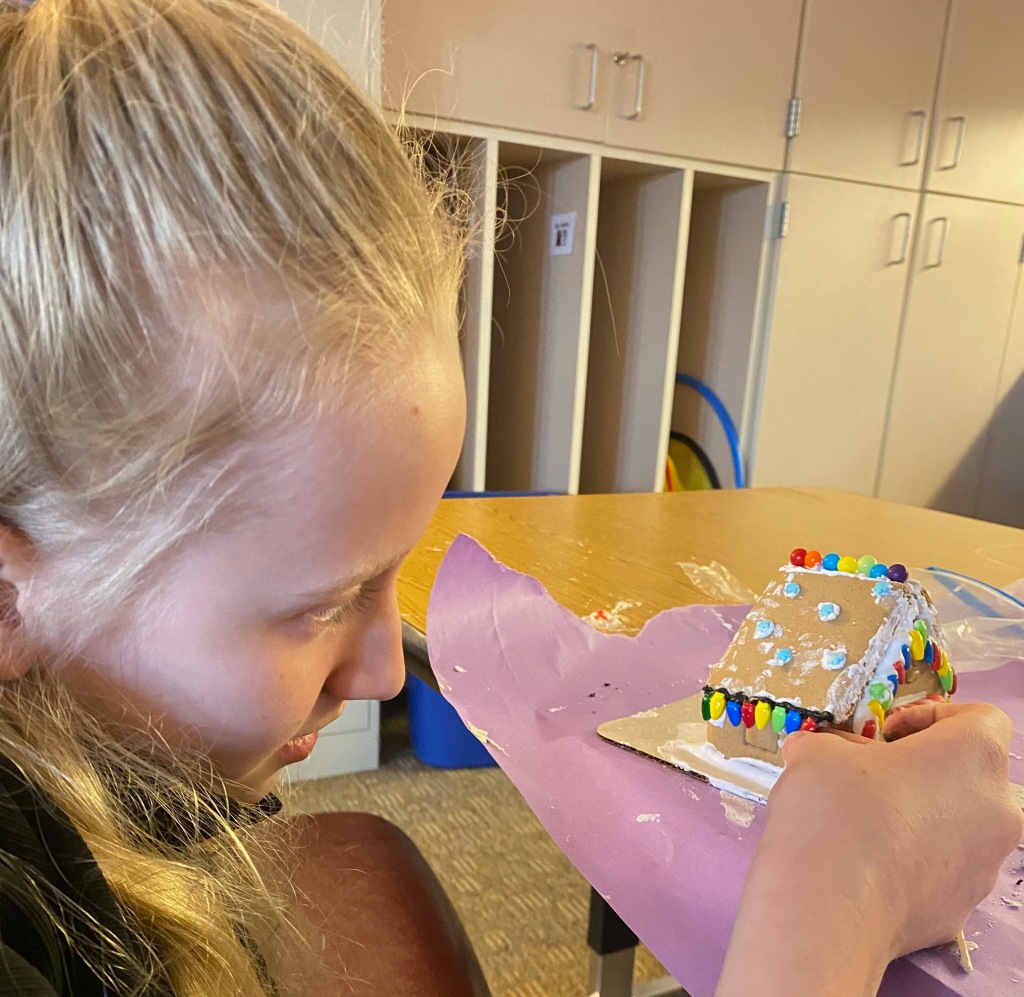
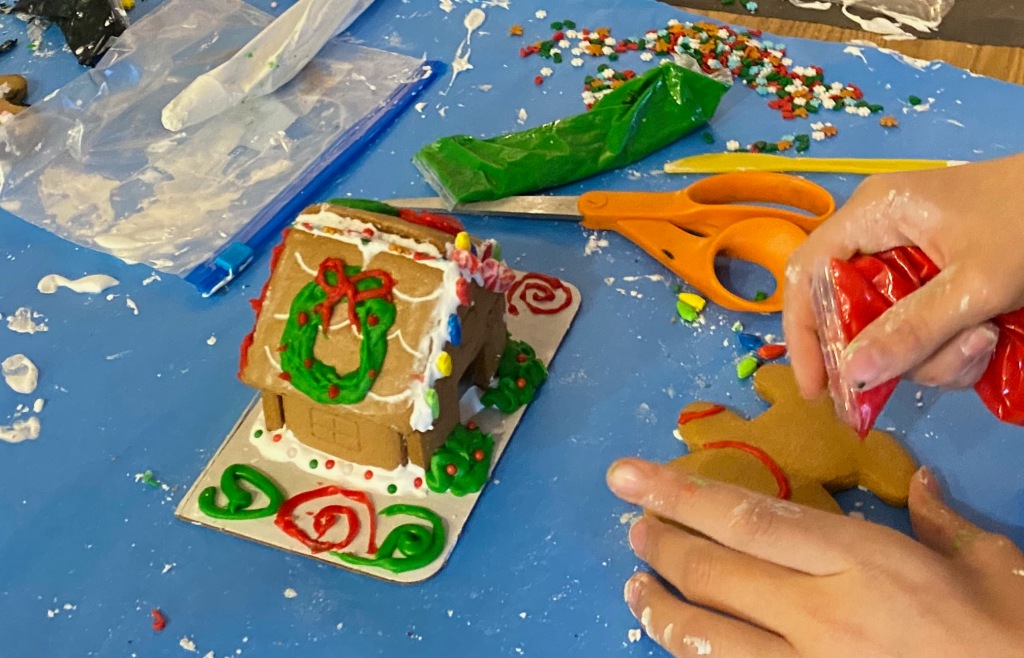









Standards Addressed
Next Generation Science Standards – Engineering
- Define a simple design problem reflecting a need or a want that includes specified criteria for success and constraints on materials, time, or cost.
- Anchor Standard #1. Generate and conceptualize artistic ideas and work.
- Anchor Standard #2. Organize and develop artistic ideas and work.
- Anchor Standard #3. Refine and complete artistic work.
Lighting Up the Kwanzaa Kinaras and Gingerbread Houses
Students learned some basics of electrical circuits using blinking LEDs. For their Kwanzaa Kinaras, they made simple LED/3V Lithium battery connections – see https://youtu.be/pIDB56RYT5M on how to do this.
To light up the inside of the gingerbread houses, the students combined 3 pre-wired LEDs (resistor built in) and a 9v battery in a series circuit (there wasn’t enough power for more than 3 in the circuit). One of the pre-wired blinking lights was placed in each of the gingerbread houses. The basics of how to do this can be found via this tutorial – https://youtu.be/DcN0Xlw7nko.
During the process of making and testing their circuits, we discussed how circuits worked, polarity, and conductive/insulting materials. The following video can help explain electrical circuits to younger students – https://youtu.be/HOFp8bHTN30
Standards Addressed
Next Generation Science Standards – Energy
- Make observations to provide evidence that energy can be transferred from place to place by sound, light, heat, and electric currents.
Lighting and Signage Using micro:bits
micro:bits were used to create signs wishing happy holidays. They were also used to light up Neopixel rings and strips.Here are some resources for the micro:bit component of the display:
- micro:bit Holiday Activities – https://microbit.org/news/2020-12-03/microbit-holiday-activities/
- Using Neopixels with the micro:bit – https://support.microbit.org/support/solutions/articles/19000130206-using-neopixels-with-the-micro-bit
- Sample Neopixel Makecode – https://makecode.microbit.org/72931-87952-73243-42587 and https://makecode.microbit.org/_VbyT1DT7uDKp
Standards Addressed
- Create programs that include sequences, events, loops, and conditionals.
- Modify, remix, or incorporate portions of an existing program into one’s own work, to develop something new or add more advanced features.
Next Generation Science Standards – Energy
- Make observations to provide evidence that energy can be transferred from place to place by sound, light, heat, and electric currents.
Math Connection
Although, I didn’t do so this year, I have included a math component to gingerbread house making in the past whereby students needed to learn about and calculate the perimeter and area of their creations (see Gingerbread House Making: A Fun and Engaging Cross-Curricular Lesson).
Dia de Muertos & Halloween Displays: A Meow Wolf-ish STREAM Lesson
I have the privilege of teaching gifted education in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Two unique characteristics of living and working here is (1) there is a strong Mexican population who have retained their beautiful culture – language, culture, food, and holiday, and (2) it is the birthplace of Meow Wolf, unique and immersive art installations with multimedia elements and a mysterious narrative throughout; whose mission is to inspire creativity in people’s lives through art, exploration, and play so that imagination will transform our worlds.
Because of these unique elements in my community, each year I ask the students to create Dia de los Muertos and/or Halloween story-driven and technology-enhanced displays which are put in the front foyers of my schools for the students and visitors to enjoy. They are project-based, high engagement (as students can draw on their individual strengths within their teams), and focus on student voice and choice. In other words, these projects become strong STREAM (Science, Technology, wRiting, Engineering, Art, Math)-based lessons which translates into being interdisciplinary. I believe all lessons should be interdisciplinary as I discuss in https://usergeneratededucation.wordpress.com/2019/01/13/all-lessons-should-be-interdisciplinary:
Standards Addressed
Due to the project’s cross disciplinary nature, standards were addressed from several disciplines:
Common Core State Standards – ELA
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.5.3 – Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, descriptive details, and clear event sequences.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.5.6 – With some guidance and support from adults, use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing as well as to interact and collaborate with others.
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.5.10 – Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences.
Science Standard
- NGSS: 4-PS3-2. Make observations to provide evidence that energy can be transferred from place to place by sound, light, heat, and electric currents.
GSS Engineering Standards
- 3-5-ETS1-1. Define a simple design problem reflecting a need or a want that includes specified criteria for success and
- constraints on materials, time, or cost.
- 3-5-ETS1-2. Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem.
ISTE Standards for Students
- Know and use a deliberate design process for generating ideas, testing theories, creating innovative artifacts or solving authentic problems.
- Develop, test and refine prototypes as part of a cyclical design process.
- Exhibit a tolerance for ambiguity, perseverance and the capacity to work with open-ended problems.
- Create original works or responsibly repurpose or remix digital resources into new creations.
National Core Arts Standards
- Anchor Standard #1. Generate and conceptualize artistic ideas and work.
- Anchor Standard #2. Organize and develop artistic ideas and work.
- Anchor Standard #3. Refine and complete artistic work.
National Standards in Gifted and Talented Education
- 1.1. Self-Understanding. Students with gifts and talents recognize their interests, strengths, and needs in cognitive, creative, social, emotional, and psychological areas.
- 1.5. Cognitive, Psychosocial, and Affective Growth. Students with gifts and talents demonstrate cognitive growth and psychosocial skills that support their talent development as a result of meaningful and challenging learning activities that address their unique characteristics and needs.
The Lesson
One of the schools where I teach (I teach at two schools) has a large Mexican (self-identifying term) population and as such, each grade has a bilingual class. My students from this school were asked to create stories and displays based on Dia de los Muertos.
The events were as follows:
- Write a Thematic Story
- Review Possible Projects for Story
- Create Artifacts and Display
Write a Story About Dia de los Muertos or Halloween
With the older students, grades 4 through 6, I reviewed the story arc and explained that they needed to include all of those elements within their stories. With the younger kids, grades 2 and 3, I talked about characters, setting, and plot and reinforced including these elements in their stories. There were 2 to 4 students per group, so they collaborated on their stories using Google Docs. What follows is one of the stories written in English and then translated into Spanish:
English Version
Spanish Version
Links to Other Stories
- The Chupacabre – 5th and 6th Graders: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1rZEbwaanXQM8V83DbmQ9FmxAze0moZjSkICJLF5SaQw/edit?usp=sharing
- Story by 4th Graders: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1XWX3tPK_eiLavBDyIY5HRhwa5YHvWvsVGVrm4Kr5at8/edit?usp=sharing
- The Haunted House – 2nd and 3rd Graders: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1YFCodaGgBIDqp-DUx1Q1_DH9mrMWO3DPOHlr62jyr_E/edit?usp=sharing
- Story by 2nd Graders: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1C5uLkTLJmBhE78xkyg01TnTgIdJQyueFacgvuIQnEss/edit?usp=sharing
Story as a Storyboard That Comic
One student requested and created his group’s story as a comic as his other two groups members wrote their story out on Google Docs. Here are a few of his cells.



The rest can be view at https://www.storyboardthat.com/portal/storyboards/cdamm/classroom-public/unknown-story3
Review Possible Projects for Story Display
For possible artifacts to create their story-driven displays and as a way to honor voice and choice, students could select from the following projects:
If interested in a specific project, I would either provide the interested student and/or group with a link to a tutorial or give a mini-lesson on it.
Create Artifacts and Display
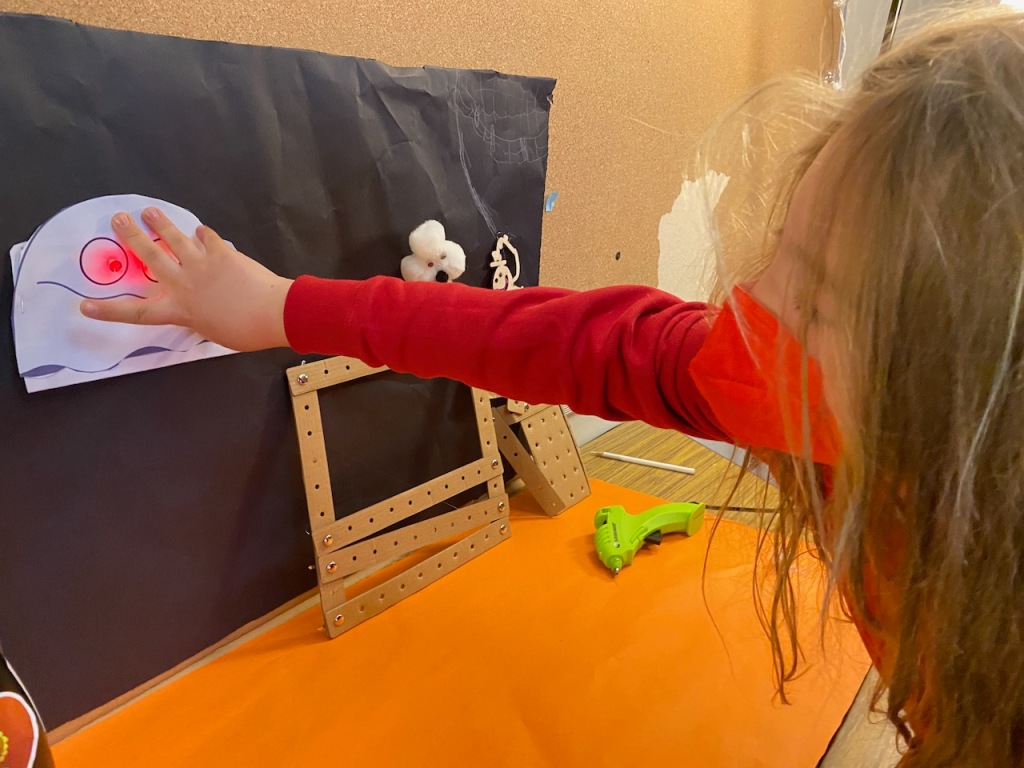
Individual groups selected a combination of the following artifacts:
- micro:bit Characters
- Neopixels – micro:bit driven
- Servos – micro:bit driven
- Sugar Skulls
- Paper Circuits Skulls and Pumpkins
- Laser Cut Objects Out of Wood
- Cardboard Construction Kits
- Jack-O-Lanterns Lit by Circuit Playgrounds
- Hummingbird Bits for Servos and Lights
Here is a slideshow of the students’ creation efforts:
Personal Reflection
The joy both my students experience throughout the lesson is palatable. I love listening to their excitement as they develop their stories. I love watching their smiles as they create their elements for their stories. I love seeing their bodies shake with excitement when their displays are complete, and I love witnessing their pride when the other students excitedly approach and comment on their displays.
Because I have students in my gifted program throughout their elementary years, I love seeing their excitement when we begin this project each year. I always try to introduce some new possibilities for their display elements each year. For example, this year I introduced and taught Hummingbird Bits which I learned about during a PD workshop this past summer. In addition, since I blog about this project each year as a means to document both students’ and my learning, I can see my own progress. Here is the blog post from the first two years I did it – Halloween Wars: An Interdisciplinary Lesson with a STEM, STEAM, Maker Education Focus. During the first year, I provided students with cookies, ping pong balls, LED lights, gummy worms, candy skeletons – no physical computing. So, for me, it is great to see my own growth, too.
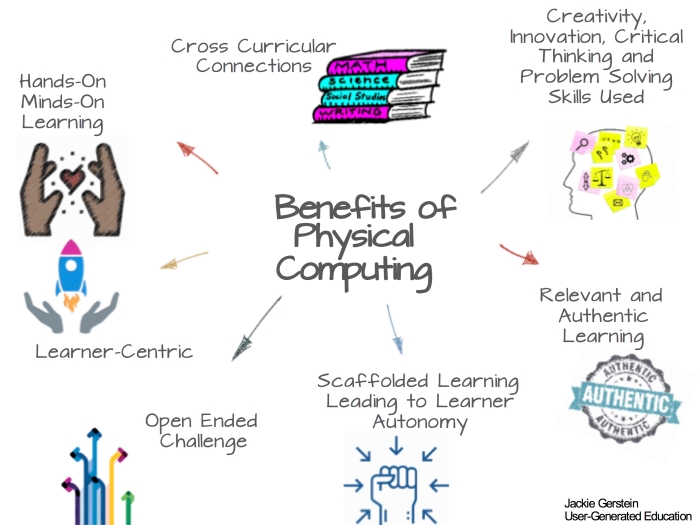
Physical Computing with micro:bits and Makecode
I am quite fond of facilitating physical computing activities with my learners as I’ve discussed in Scratch and Makey Makey Across the Curriculum . For that post I created the following graphic to represent the benefits of physical computing. I think it is important to extend the use of coding and microcontrollers into creating physical objects for the following reasons:
Standards Addressed
ISTE Standards for Students
- Know and use a deliberate design process for generating ideas, testing theories, creating innovative artifacts or solving authentic problems.
- Develop, test and refine prototypes as part of a cyclical design process.
- Exhibit a tolerance for ambiguity, perseverance and the capacity to work with open-ended problems.
- Create original works or responsibly repurpose or remix digital resources into new creations.
Next Generation Science Standards
- Analyze data from tests to determine similarities and differences among several design solutions to identify the best characteristics of each that can be combined into a new solution to better meet the criteria for success.
- Develop a model to generate data for iterative testing and modification of a proposed object, tool, or process such that an optimal design can be achieved.
micro:bit Activities
The following slide deck contains the list of micro:bit activities completed by my summer campers. It includes the Makecode for the more advanced projects:
Here are examples of student projects:
Lip Syncing Characters Using micro:bits and Hummingbirds
I am quite fond of facilitating physical computing activities with my learners as I’ve discussed in Scratch and Makey Makey Across the Curriculum . For that post I created the following graphic to represent the benefits of physical computing. I think it is important to extend the use of coding microcontrollers into making physical objects for the following reasons:

Lip Syncing Characters with a micro:bit and a Servo
I was excited to find Cecilia Hillway‘s (she’s so very talented!) Lip-Syncing Characters With Micro:bit – https://www.instructables.com/Lip-Syncing-Characters-With-Microbit/. Here is her video overview of her processes:
. . . and here are some examples of what my students did over the school year and what Cecilia’s kids did this summer:
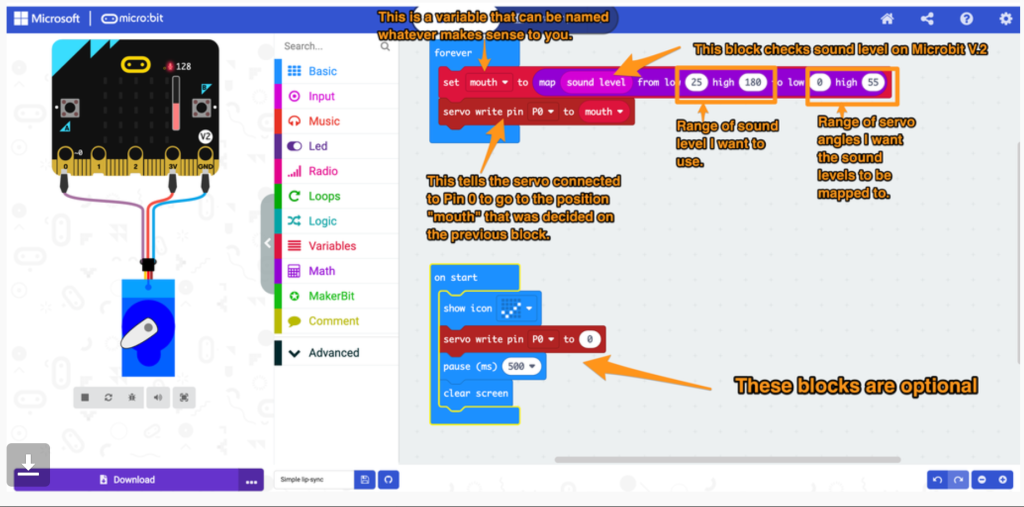
Cecilia’s provided a Makecode graphic for the project:
I recreated this Makecode – https://makecode.microbit.org/_aRfexJ44aEpk
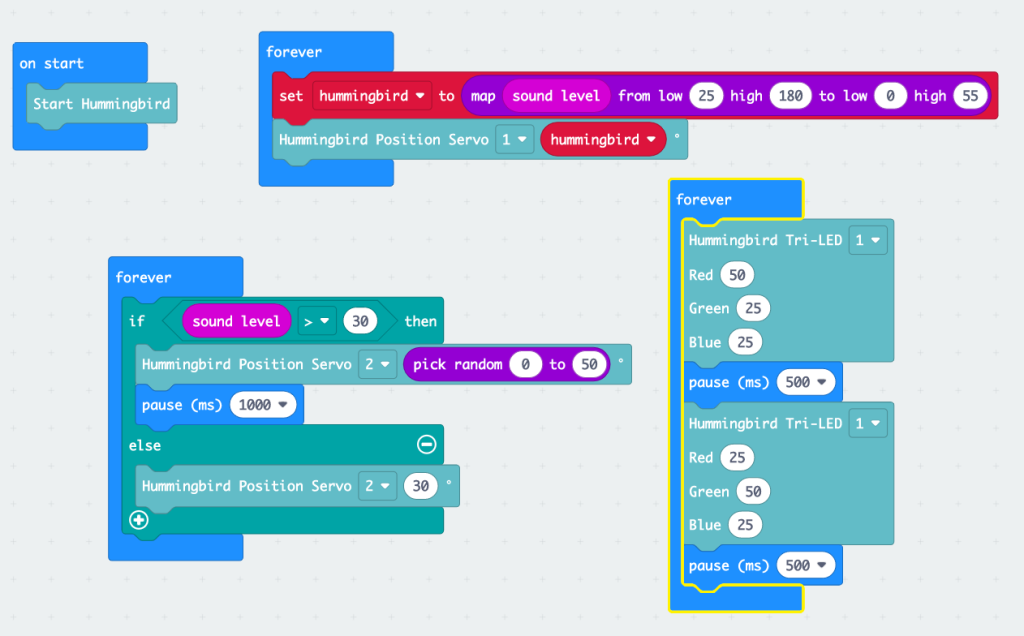
Lip Syncing Characters with a Hummingbird
A Hummingbird by Birdbrain is a kit of lights, sensors, and motors which allows students to create personally meaningful robots out of any materials. As part of her Instructables, Cecilia described her use of Hummingbird to add more features to the Lip Syncing Characters. It was a bit complicated for me so I used the kit to add a second servo to have her arm move and a flashing light to highlight my character’s name.
With the help of the folks from Codejoy, a Makecode was created for this project.
Here is the makecode – https://makecode.microbit.org/_1Ex1vYcqbF0r
The Joy of Watching a Lesson Come Alive
Number one on my love list of teaching is spending time with my fantastic students. High on my list is also my love of designing and creating learning activities for my students. I get such joy in seeing my designs come to life in the hands of my learners. Recently, I designed a pinball machine using a pizza box, Strawbees, Makedo screws, and an optional micro:bit scoreboard. The full directions can be found at: https://www.instructables.com/Cardboard-Pinball-Machine-Using-a-Pizza-Box-Strawb/.
I got to test my new learning activity with my summer campers during my Toy Making camp. As is usual, when kids get to jump in and try the activity out for themselves, they far exceeded my vision and expectations for it.
As I observed the campers making the pinball machine, I found such joy in witnessing:
- 100% engagement. All students were actively and joyfully engaged. It reinforced my belief that there is a human need to create. I wrote about this in The Magic of Making: The Human Need to Create.
- Their creativity. I was in awe about the directions they took with this; how much they added their selves to the base project.
- Their ability to create the project without direct instruction. About half of them were able to just fly with it without my assistance; by just studying my prototype.
- Their eyes light up when their projects worked as they envisioned them.
- Their interest in their peers’ projects.
- How valuable experiential learning is. I wrote about this in The Imperative of Experiential and Hands On Learning: